Measurement device and method for measuring and generating a topographic map of the preretinal space
Description: The presented research was conducted as a part of the CAVRI (Computer Analysis of VitreoRetinal Interface) Project. This project is based on interdisciplinary cooperation between the scientists from Poznan University of Technology (PUT) with ophthalmology specialists from the Poznan University of Medical Sciences (PUMS).
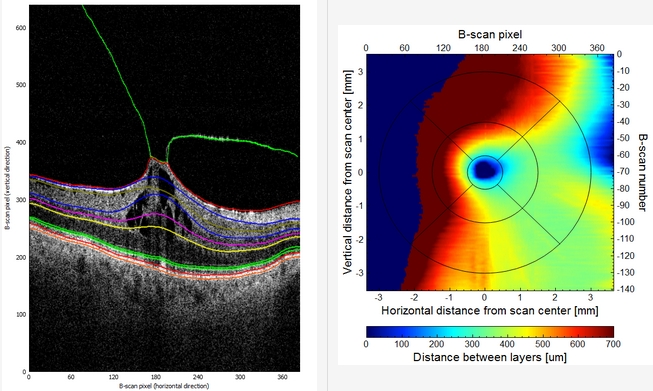
This invention presents the results of studies concerning the automatic investigation of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) retina images. The disorders at the border of the human eye retina and vitreous (called VitreoRetinal Interface – VRI) can cause severe retinal damage and carry a high risk of vision loss. Their early detection and accurate assessment are beneficial for successful therapy.
ABSTRACT and APPLICATIONS:
The object of the invention is a device for measuring the preretinal space from OCT or OCTA images of the retina and a method for measuring the parameters of the preretinal space and a topographical map of this measurement in ophthalmology and other specialities examining the visual system for diagnosis, monitoring of disease progression and qualification for surgery (e.g. vitrectomy) and intraoperative assessment.
The proposed solutions were tested on a specially prepared database of OCT images prepared by inventors from PUMS. The authors from PUT prepared a custom software called OCTAnnotate to provide the ophthalmology experts with specialized tools to evaluate the VitreoRetinal Interface. The methods proposed were also implemented in this open-source software.
The obtained segmentations were the basis for automated parameterization of pathologic retina structure.
The devised parameters valuable for clinicians are the volume of the preretinal space, the area of attachment of the vitreous to the retina surface, the contour of the fovea, and the parameters of the fovea pit shape.
The developed techniques allowed for the generation of profiles of VMT disorder in the form of data or images understandable to clinicians.
The results of experiments show that the designed algorithms provide valuable information for quantitative analysis of the VMT pathology stage and its progress in a long-term observation.
ADVANTAGES and FEATURES:
The proposed system based on fully convolutional neural networks allows for achieving preretinal space segmentation accuracy of up to 96%.
TECHNOLOGY READINESS LEVEL:
TRL8 - research and demonstration of the final version of the technology completed
TRL9 - development phase (applications of Artificial Intelligence to medical image analysis)
Organisation: Poznan University of Technology, Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Innovator(s): Adam Mirosław Dąbrowski (PUT), Tomasz Marciniak (PUT), Agnieszka Anna Stankiewicz (PUT), Marcin Stopa (PUMS), Elżbieta Anna Marciniak (PUMS), Piotr Rakowicz (PUMS)
Category: Medicine, Biotechnology and Medical Devices
Country: Poland
